 The formate ion, (CHO2-), is related to the acetate ion and forms ionic salts with many metal ions. Assume that 9.7416 g of M(CHO2)2 (where M represents the atomic symbol for a particular metal) are dissolved in water. When a solution of 0.200 M sodium sulfate is added, a white precipitate forms. The sodium sulfate solution is added until no more precipitate forms, then a few excess milliliters are added. The precipitate is filtered, washed, and dried. It has a mass of 9.389 g. The filtrate is placed aside. The formate ion, (CHO2-), is related to the acetate ion and forms ionic salts with many metal ions. Assume that 9.7416 g of M(CHO2)2 (where M represents the atomic symbol for a particular metal) are dissolved in water. When a solution of 0.200 M sodium sulfate is added, a white precipitate forms. The sodium sulfate solution is added until no more precipitate forms, then a few excess milliliters are added. The precipitate is filtered, washed, and dried. It has a mass of 9.389 g. The filtrate is placed aside.
A potassium permanganate solution is standardized by dissolving 0.9234 g of sodium oxalate in dilute sulfuric acid, which is then titrated with the potassium permanganate solution. The principal products of the reaction are manganese(II) ion and carbon dioxide gas. It requires 18.55 mL of the potassium permanganate solution to reach the end point, which is characterized by the first permanent, but barely perceptible, pink (purple) color of the permanganate ion.
The filtrate from the original reaction is diluted by pouring all of it into a 250-mL volumetric flask, diluting to the mark with water, then mixing thoroughly. Then 10.00 mL of this diluted solution is pipetted into a 125-mL Erlenmeyer flask, approximately 25 mL of water is added, and the solution is made basic. What volume of the standard permanganate solution will be needed to titrate this solution to the end point? The principal products of the reaction are carbonate ion and manganese(IV) oxide.
Source: Burness, James H. The use of "marathon" problems as effective vehicles for the presentation of general chemistry lectures. J. Chem. Educ. 1991 68 919.
The relative average masses of atoms of the elements are given in the periodic table.
Two compounds that contain only phosphorus and an unknown element X have ratios mass X/mass P of 1.84 and 3.06. Assuming that both of these compounds consist of molecules that contain only one atom of phosphorus per molecule, answer the following questions.
1. What are the formulas of the two compounds?
2. What are the symbol and name of element X?
3. Element X has only one stable isotope. How many neutrons are there in an atom of X?
Assume that a reaction occurs in which unknown substances W and X react to form unknown substances Y and Z. From the information below, determine the mass of substance Y that will be formed if 45.0 grams of substance W reacts with 23.0 grams of substance X. (Assume that the reaction between W and X goes to completion.)
(a) Substance W is a gray solid that consists of an alkaline earth metal and 37.5% carbon by mass. A sample of substance W that contains 4.0 x 1019 formula units has a mass of 4.26 milligrams.
(b) 47.9 grams of substance X contains 5.36 grams of hydrogen and 42.5 grams of oxygen.
(c) When 10.0 grams of substance Y is burned in excess oxygen, 33.8 grams of carbon dioxide and 6.92 grams of water are produced. An instrumental method determined the molar mass of substance Y is 26 g/mol.
(d) Substance Z is the hydroxide of the metal in substance W.
A utility company changed its gas for domestic use from water gas (about 50 percent by volume hydrogen, H2, and 50 percent carbon monoxide, CO) to coke-oven gas (about 30 percent hydrogen and 70 percent methane, CH4) without altering burners or pressure. A lawsuit was filed against the utility by a man who claimed that he was made ill by the new mixture due to excess carbon monoxide escaping unburned from a lighted cooking stove.
The main parts of a typical gas burner are shown in the following diagram.

Under proper conditions, hydrogen is known to burn to H2O, carbon monoxide to CO2, and methane to H2O and CO2.
2 H2 + O2 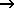 2 H2O 2 H2O
2 CO + O2 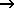 2 CO2 2 CO2
CH4 + 2 O2 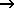 CO2 + 2 H2O CO2 + 2 H2O
If oxygen is limited, carbon monoxide may be formed from methane.
2 CH4 + 3 O2 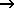 2 CO + 4 H2O 2 CO + 4 H2O
Which of the following should be most useful in investigating the possibility of CO formation due to oxygen deficiency? Explain.
- The law that gases combine in fixed ratios by volume.
- The table of atomic weights.
- The laws relating pressure, volume, and temperature of gases.
- The laws of chemical equilibrium.
- The law of definite proportions by weight.
The complainant's attorney held that the utility company should have increased the gas pressure in the mains. What would have been the most likely result of increasing the gas pressure?
- It would have allowed a more complete combustion.
- The combustion would have been more complete, but a large waste of gas would have resulted.
- It would have rectified the condition but would have produced a flame of a lower temperature.
- It would have made the combustion even less complete.
Explain the reasoning for your answer as well as why you eliminated the other alternatives.
Source: Adapted from Handbook on Formative and Summative Evaluation of Student Learning by B. S. Bloom, J. T. Hastings, & G. F. Madaus, McGraw Hill, 1971, p 617.
|



