
The coordination geometry and coordination number of a cation usually, but not always, depends on the radius ratio. As the radius ratio increases, coordination numbers increase. A given coordination number is usually found when the ions involved in the structure have a radius ratio that falls into a range that is characteristic of that geometry.
Click the button on the right to view an animation. The links above will display definitions.
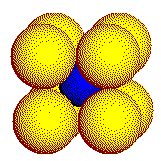
Cube
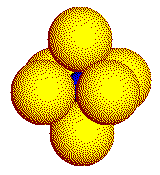
Octahedron

Tetrahedron
Cation
Size
Anion
Size
Ranges
of Radius Ratios
For
tetrahedral geometry:
0.225 < r+/r- < .414
0.225 < r+/r- < .414
For
octahedral geometry:
0.414 < r+/r- < 0.732
0.414 < r+/r- < 0.732
For
cubic geometry:
0.732 < r+/r- < ~1
0.732 < r+/r- < ~1
From
the Tetrahedron
From
the Octahedron
From
the Cube



Copyright ©
2003
by: Journal of Chemical Education Software
by: Journal of Chemical Education Software