A Lewis diagram depicts a molecule using an element symbol to represent the nucleus and core electrons of each atom. Lines for electron-pair bonds and dots for unbonded electrons represent valence electrons.
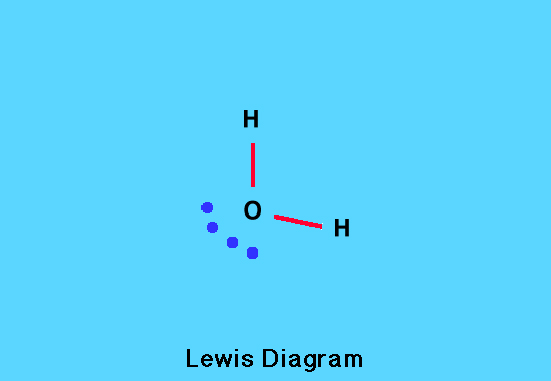
Water
Each of the two hydrogen atoms in a water molecule contributes a single valence electron and the oxygen atom contributes six, giving a total of eight valence electrons. These are arranged in an octet (eight electrons) around the oxygen atom; two electrons in each O—H bond and the remaining four as two lone pairs.
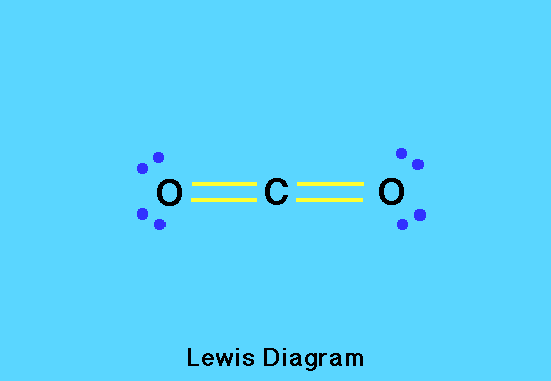
Carbon Dioxide
Each of the two oxygen atoms in a carbon dioxide molecule contributes six valence electrons and carbon four for a total of 16 electrons. These are arranged with two pairs in each of two double bonds giving an octet around the carbon atom. The remaining electrons are lone pairs on the two oxygen atoms, each of which also has an octet of electrons.
Hydrogen Cyanide
In hydrogen cyanide, HCN, there are four valence electrons are contributed by carbon, five valence electrons contributed by nitrogen and one electron from hydrogen for a total of ten. Octets around C and N can be achieved by sharing six electrons (a triple bond) between the atoms, having a single bond to hydrogen, and one lone pair of electrons on nitrogen.
