LUMO is the acronym for Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital. Valence electrons from the atoms in the molecule are distributed among the molecular orbitals on the basis of potential energy. The lowest energy molecular orbitals are filled first. After all of the electrons have been assigned to molecular orbitals, the lowest-energy orbital that does not contain any electrons is the LUMO.
œ = one unpaired electron
œ![]() = two paired electrons.
= two paired electrons.
Hydrogen MO Diagram
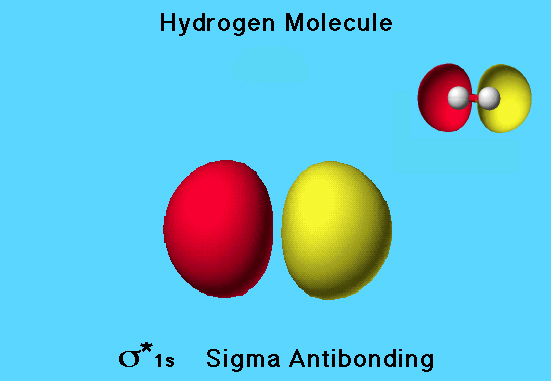
For the hydrogen molecule, there are two molecular orbitals formed by the combination of the 1s orbitals of each atom. Since there are only two valence electrons, both go into the orbital having the lower energy. The remaining orbital, the σ* 1s (sigma antibonding) orbital, is unoccupied and is thus the LUMO.

Hydrogen LUMO
This is a view of the σ* 1s (sigma antibonding) orbital, which is the LUMO for the hydrogen molecule.
Nitrogen MO Diagram
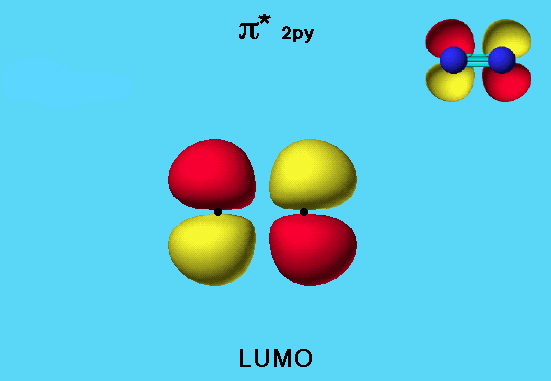
This is the molecular orbital energy diagram for the nitrogen molecule, which has a total of 10 valence electrons. The lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals are the π* (pi antibonding) orbitals (2py and 2pz). These orbitals are degenerate (have the same energy), so both are LUMOs for nitrogen.

Nitrogen LUMO
The <pi>* 2py & 2pz (pi antibonding) orbitals are both LUMOs for this molecule. The <pi>* 2py orbital is shown below. The <pi>* 2pz orbital is identical in both shape and energy, but rotated by 90° so that it is perpendicular to the surface of the screen.