HOMO is the acronym for Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital. Valence electrons from atoms are distributed among the molecular orbitals on the basis of potential energies. The lowest energy orbitals are filled first. The last orbital to be filled or partially filled is known as the HOMO. Electrons in orbital diagrams are represented as:
œ = one unpaired electron
œ![]() = two paired electrons
= two paired electrons
Hydrogen MO Diagram
The hydrogen molecule has two electrons and two molecular orbitals. Only the lower energy orbital, s 1s (sigma bonding) orbital, is occupied. It is the HOMO.

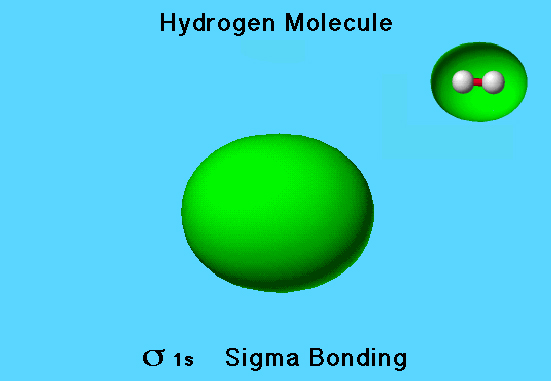
Hydrogen HOMO
This is a view of the s 1s (sigma bonding) orbital, which is also the HOMO.
Nitrogen MO Diagram
This is the molecular orbital energy diagram for the nitrogen molecule, which has a total of 10 valence electrons. The highest-energy molecular orbital that is occupied, the HOMO, is the s 2px (sigma bonding) orbital; in the diagram, its energy level is surrounded by a red box.

Nitrogen HOMO
The s 2px (sigma bonding) molecular orbital is the HOMO for the nitrogen molecule.
Notice that electron density is concentrated between the nuclei (in the blue region) attracting the nuclei and holding them together. This is therefore a bonding molecular orbital.
